-
Featured services
Harness innovation to deliver value
Ensure short-term stability as you design a roadmap for new use cases in your industry with emerging technologies.
Explore Connected Industries -
Services
View all services and productsLeverage our capabilities to accelerate your business transformation.
-
Services
Network as a Service
Popular Products
-
Private 5G
Our turnkey private 5G network enables custom-built solutions that are designed around unique use cases and strategies, and deployed, run and optimized through a full network-as-a-service model.
-
Managed Campus Networks
Our Managed Campus Networks services transform campus networks, corporate area networks and interconnected local area networks, and connect smart places and industries.
-
-
Services
Cloud Services
Popular Products
-
Cloud Migration and Transformation Services
Access the people, processes and technologies you need to deliver cloud migration projects that improve your return on investments.
-
Site Reliability Engineering Services
Get the most from your cloud investments when you harness our Site Reliability Engineering Services to support app development and lifecycle management.
-
-
Services
Edge as a Service
Client stories
-
Penske Entertainment and the NTT INDYCAR SERIES
Together with Penske Entertainment, we’re delivering digital innovations for their businesses – including INDYCAR, the sanctioning body of the NTT INDYCAR SERIES – and venues such as the iconic Indianapolis Motor Speedway, home to the Indianapolis 500.
-
Using private wireless networks to power IoT environments with Schneider Electric
Our combined capabilities enable a secure, end-to-end digital on-premises platform that supports different industries with the benefits of private 5G.
-
-
Services
Technology Solutions
Client stories
-
Services
Global Data Centers
-
Services
Digital Collaboration and CX

IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Datacenter Services 2023 Vendor Assessment
We provide a new kind of intelligent infrastructure to deliver better outcomes through technology.
Get the IDC MarketScape -
-
-
Insights
Recent Insights
-
The Future of Networking in 2025 and Beyond
-
Using the cloud to cut costs needs the right approach
When organizations focus on transformation, a move to the cloud can deliver cost savings – but they often need expert advice to help them along their journey
-
Make zero trust security work for your organization
Make zero trust security work for your organization across hybrid work environments.
-
-

Copilot for Microsoft 365
Everyone can work smarter with a powerful AI tool for everyday work.
Explore Copilot today -
-
Global Employee Experience Trends Report
Excel in EX with research based on interviews with over 1,400 decision-makers across the globe.
Get the EX report -
Discover how we accelerate your business transformation
-
About us
CLIENT STORIES
-
Liantis
Over time, Liantis – an established HR company in Belgium – had built up data islands and isolated solutions as part of their legacy system.
-
Randstad
We ensured that Randstad’s migration to Genesys Cloud CX had no impact on availability, ensuring an exceptional user experience for clients and talent.
-
-
CLIENT STORIES
-
Liantis
Over time, Liantis – an established HR company in Belgium – had built up data islands and isolated solutions as part of their legacy system.
-
Randstad
We ensured that Randstad’s migration to Genesys Cloud CX had no impact on availability, ensuring an exceptional user experience for clients and talent.
-
-
CLIENT STORIES
-
Liantis
Over time, Liantis – an established HR company in Belgium – had built up data islands and isolated solutions as part of their legacy system.
-
Randstad
We ensured that Randstad’s migration to Genesys Cloud CX had no impact on availability, ensuring an exceptional user experience for clients and talent.
-

NTT DATA and HEINEKEN
HEINEKEN revolutionizes employee experience and collaboration with a hybrid workplace model.
Read the HEINEKEN story -
- Careers
5G networking – connecting a data-driven world
By Nadeem Ahmad,Senior Vice President, Technology strategy
What is 5G networking?
Accelerate digital transformation with an enabling technology driven by business outcomes
By now, you have heard or read about 5G networking at length. We all have a basic understanding that 5G is the fifth generation of cellular wireless technology and the new standard for mobile communications. 5G offers low latency, higher data-transfer speed and the capacity to carry a larger number of connections than previous standards.But why is it interesting, especially for the enterprise, and why have you been reading more about it lately?
Use cases and the 5G triangle
The 5G network is designed to address various use cases across verticals, all within the same network and using the enhancements or attributes of that network.5G offers three fundamental performance enhancements:
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) will deliver ongoing improvements to mobile data connectivity, characterized by increased throughput and improved coverage and capacity. It will also enable fixed wireless access (FWA) services which can compete with fixed broadband.
- Ultra-reliable and low-latency communications (URLLC) will enable the mass adoption of internet of things (IoT) services across many verticals. This results in reliable indoor coverage and the ability to support a very high density of devices.
- Massive machine-type communications (mMTC) will offer connectivity for mission-critical applications that require very low latency and high reliability and security.
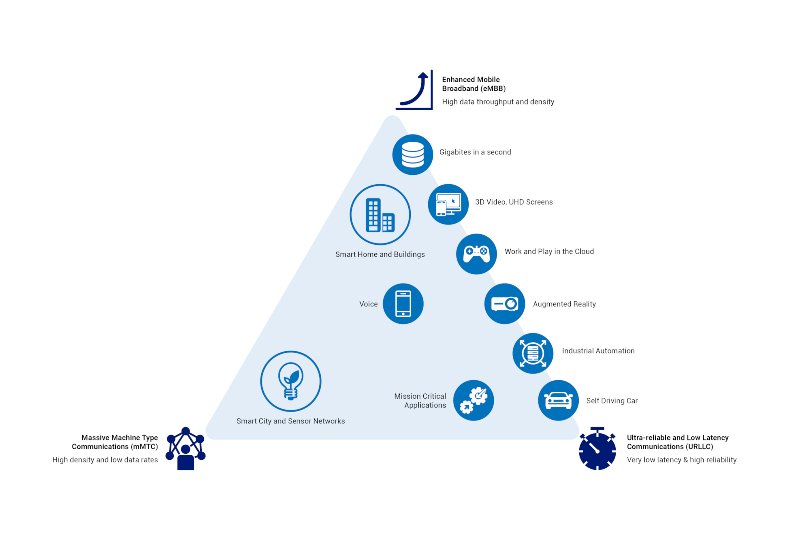
The 5G triangle in Figure 1 shows examples of these use cases. The use case is placed in the triangle near one or more of the enhancements that enable the use case or make it more effective.
Figure 1: The 5G triangle
Source: International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication (ITU-R) IMT-2020 requirements
Here are some scenarios:
- Transporting growing volumes of data: You need enhanced broadband to cope with the limited time available to transport an ever-growing amount of data – so eMBB (top of the triangle) will help you download gigabytes of data in seconds.
- Mission-critical applications: To address the challenges of autonomous (self-driving) vehicles, you need ultra-reliable low latency. URLLC (bottom right of triangle) will help enable mission-critical applications where a millisecond of delay can cost money or even compromise the safety of pedestrians or cyclists.
- Managing devices and sensors: To run a smart city, you need to be able to increase the density of sensors and devices. In this use case, you can use the mMTC technology (lower left of triangle), so 5G can handle the billions of sensors and devices, and allow them to communicate more efficiently and freely.
- Prioritizing network traffic: Network slicing is a technology component of 5G that helps prioritize traffic and enhance security. It provides for dedicated logical or virtual networks for specific functional requirements — for example, an eMBB slice, URLLC slice or IoT slice. It will be interesting to see how this technology can be used as it evolves.
What’s interesting about 5G is that it’s the use cases that determine the boundaries of the triangle. In other words, the design of 5G is business-outcome driven.
The big difference
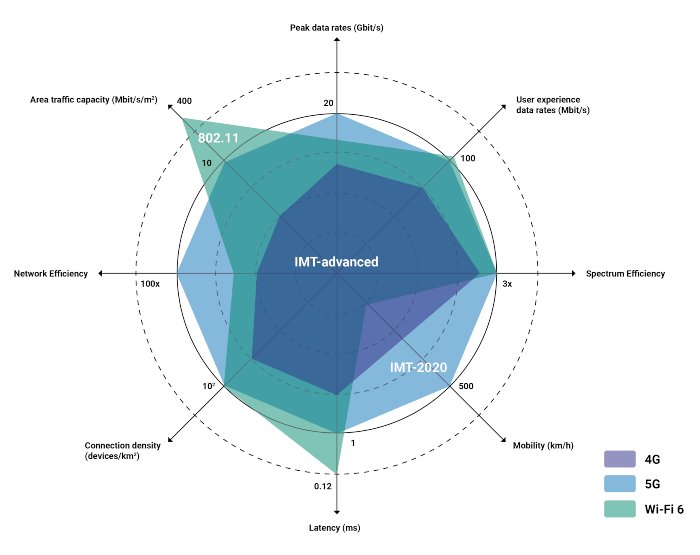
Previous generations of mobile networks were much more technology- and carrier-oriented. With 5G networking, the emphasis is more on enterprise needs, which is the focus of this review.We do not see 5G suddenly replacing 4G/LTE or Wi-Fi 6. It is not an either-or situation. Rather, we believe these technologies will co-exist in the short to medium term.
As Figure 2 shows, each will have a part to play, depending upon the technical and commercial requirements of an enterprise campus. Keep in mind there’s already a 4G/LTE infrastructure in place that can be used as a jumping-off point for 5G-driven use cases that need a greater order of magnitude in performance improvements.
5G networking will be a true enabler for business growth as it was designed to improve performance in these three key areas:
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)
- Massive machine-type communications (mMTC)
- Ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC)
Figure 2: Coexistence, not competition: 4G, 5G, Wi-Fi 6
Source: Wireless Broadband Alliance
5G networks will enable and accelerate digital transformation
Given that 5G will provide an order of magnitude of performance in a sort of evolution of mobility connectivity, it will be a true enabler and accelerator for many modern digital transformation applications across the IoT, data and artificial intelligence (AI) realms.
5G is also a type of mobile network. It can be set up as a public network owned by the carrier, or licensed as a private network, with a special frequency spectrum and a local restriction (for example to a factory site) that’s owned by an enterprise or institution.
A private 5G strategy will depend on the rollout of private 5G licensing in an enterprise’s particular country. The Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) offers a view of private 5G licensing regulations and allocations by country.
Why 5G now?
It’s all about the (private) data
Public 5G networks are essentially an evolution and extension of existing wireless communications networks that will take fixed mobile convergence to the next level. Typical use cases include wireless connectivity for branch offices and mobile workers, or next-generation connectivity for vehicles.
Things get interesting when we look at the area of private 5G networks, where the spectrum – and hence the network – is owned by an enterprise or institution and can be restricted to a certain area. Depending on where the organization’s facilities are located, and the maturity of their country’s specific licensing regulations, private 5G can be very impactful for enterprises.
Private 5G networks are a gamechanger
Private 5G changes the game by enabling enterprises to drive digitalization and decisively improve data-based business models. Private 5G will help support the platforms and services enterprises purchase. Just as importantly, it will give enterprises time-critical production control and data-supported decision-making in real time.
These private, local 5G networks can improve on the services offered by public networks, especially when Wi-Fi is not viable in a large campus or an expansive logistics environment. Dedicated 5G networks will extend connectivity beyond the campus wireless local area network (WLAN). They’ll also fulfil the technical requirements organizations have for improved performance, company control or security, and commercial requirements for lowering airtime spend and coverage-deployment costs.
We find these requirements usually lead to some interesting use cases in transportation and smart cities, and particularly in secure facilities or the supply chain area of manufacturing plants. The use cases for 5G become quite compelling when applied to large, campus-wide environments. This is because the 5G network enables more widespread coverage and connectivity across a plethora of devices transmitting large volumes of data that must be secure and controlled.
Connecting a data-driven world
The industry tagline – 'It’s all about the data' – is applicable here because 5G is not only about wireless connectivity.
We’ve looked at the order of magnitude of performance improvements relating to data throughput, connection density and, of course, lower latency. If you put 5G and those performance improvements in the context of areas like IoT and AI, 5G will allow businesses to derive real value from the billions of connected devices communicating, leveraging intelligence, delivering new insight and optimizing in real time. Think of the modern IoT and AI-driven applications that will need to download large volumes of data as fast as possible for effective prediction and automation in true real time.
In addition, sustained low latency is deemed the primary 'killer app' for 5G. This is what enterprises – particularly in verticals such as manufacturing – will increasingly come to realize as they conduct strategic assessments as part of their digital transformation initiatives. They’ll see that 5G is superior and better suited to their long-term needs
Again, 5G is not only about wireless connectivity. It can be a catalyst for a new paradigm of computing to support new data demands across core to edge to cloud, and extract the true value of data generated across the chain. We anticipate real 5G network transformation will leverage the AI revolution, edge explosion and cloudification.
What does this mean for enterprises?
In reality, there’s a lot of hype and confusion about the performance benefits and range of variations of 5G from an enterprise perspective.Firstly, many of the innovations will not come into play until the next revision (R16) of the standard in the coming year or two (we are only seeing R15 in use today). There may also be limited coverage for ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC). Secondly, 5G devices to date have been scarce or expensive, so the commercial model is uncertain – especially when considering the rapid obsolescence of first-generation devices. Finally, most IoT implementations do not need 5G.
That said, now is not the time for enterprises to wait.
Now is the time to start planning for 5G adoption
Early private 5G adoption will begin soon. If enterprises want to lead, they need to start planning. Let’s look briefly at the areas that will start ramping up in the coming year or two.
Market timing will depend largely on the maturity of the market and the business cases that support fully utilizing the power of 5G. Of course, some markets will be faster to emerge than others, especially when 5G technology is close enough to the existing services.
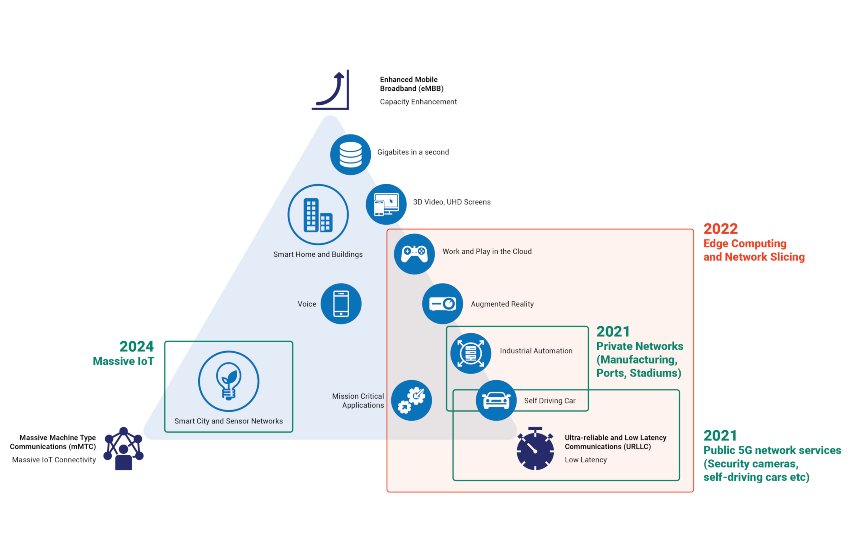
These services will be typified by private 5G networks in the first case, starting in 2021. This will be driven by high demand for the new features 5G networks provide – like lower latency or control over power consumption or speed/data rates. We’re likely to see public 5G in the latter part of the year (similar to 4G that’s in existence today, just better with 5G).
Other use cases, such as edge-compute-driven services (2022) and massive IoT (2024), will take a little more time to develop as the industry explores the new features of 5G and applies them to existing or new challenges.
Figure 3: 5G network timing
Source: International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication (ITU-R) IMT-2020 requirements
Work with providers that will help you realize the benefits of 5G networks
As adoption continues, enterprises must work with a trusted provider and partner that understands the security ramifications of a connectivity technology that enables more data to be transmitted across more devices than ever before.
Enterprises should look for partners developing a Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) framework that’s focused on the edge-to-cloud network fabric. Ultimately, they need to address:
- Mobile and fixed access to the cloud
- Edge compute platform for the network edge
- Edge compute platform for the customer edge
The goal should be to provide a seamless, end-to-end, software-defined management layer that adds functionality and flexibility to enable domestic and global expansion.
Providers with a strong partner ecosystem that can help implement and manage 5G network solutions across the value chain – from device to network to data to applications – are in the best position to assist enterprises with taking full advantage of the benefits public and private 5G will bring to the world.

NTT Private 5G: A global private network delivering speed, control, security and total coverage. Finally.